Load Product Catalog
Azure Cosmos DB is a globally distributed, multi-model database service for any scale. The Azure Cosmos DB for MongoDB supports Vector Search, which allows you to search for documents based on their similarity to a query document.
In this lab, you will load the product catalog data into Azure Cosmos DB. The product catalog will be used by the chatbot to answer questions related to the products in the catalog.
The product catalog data is shared in a CSV file. You will be writing a custom script to convert the CSV file to JSON format and then load the JSON data into the Cosmos DB.
Setup the lab environment
-
Open repo in
VS Codeand then openTerminial->New Terminal. Navigate to the lab folder~/labs/02-LAB-02/2-Load-Data/startwithin the repository.cd labs/02-LAB-02/2-Load-Data/start
The ~/labs/02-LAB-02/2-Load-Data/completed folder contains the completed solution for this lab. Please use start folder to carry out the exercise. You can compare your code with the files in completed folder if your code does not run correctly.
-
Check
.envfile has correct configurations. Placeholder string should be all replaced in earlierLab Setupstep. -
In Visual Studio Code, open a terminal window and navigate to
startfolder. -
To install the required packages, execute the following command in the terminal window:
npm install
Prepare the data set
The quality of the dataset feeding into the LLM model makes a big difference. While it is typically the responsibility of the data team, there may be various conversions and integrations required to format the dataset. Let's take a look at the product dataset and see if any modifications are needed before loading it into Cosmos DB.
The product data set is located in the data\product.csv file. It has the following fields: id,categoryId,categoryName,sku,name,description,price,tags. The tags field is a JSON array of strings.
-
Here is a snapshot of the
product.csvfile: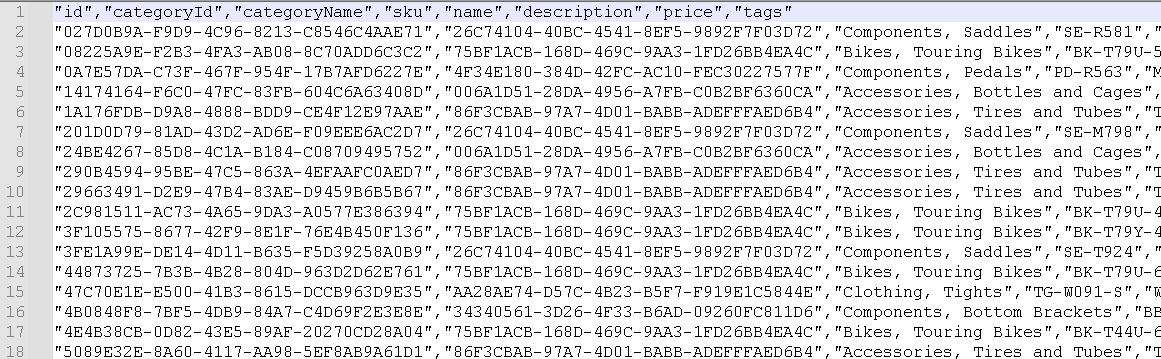
-
The first step is to convert the CSV file to JSON format. Open the
convert.jsfile and paste the following code. This will parse the CSV file and generateproduct.jsonfile with the data.const fs = require("fs");
const path = require("path");
const rootDir = "data";
// Read CSV file
const csvFilePath = path.join(rootDir, "product.csv");
const csvData = fs.readFileSync(csvFilePath, "utf8");
// Convert CSV to JSON
function csvToJson(csv) {
const lines = csv.trim().split("\n");
const headers = lines[0]
.split(",")
.map((header) => header.replace(/"/g, ""));
const jsonData = lines.slice(1).map((line) => {
const values = line
.split(/,(?=(?:(?:[^"]*"){2})*[^"]*$)/)
.map((value) => value.replace(/"/g, ""));
const obj = {};
headers.forEach((header, index) => {
if (header === "tags") {
// Decode the JSON string
obj[header] = JSON.parse(values[index].replace(/'/g, '"'));
} else {
obj[header] = values[index];
}
});
return obj;
});
return JSON.stringify(jsonData, null, 2);
}
const json = csvToJson(csvData);
// Write JSON to file
const jsonFilePath = path.join(rootDir, "product.json");
fs.writeFileSync(jsonFilePath, json, "utf8");
console.log("CSV file has been converted to JSON file successfully."); -
Save the
convert.jsfile. Run the following command in the terminal window to execute the script:node convert.js -
Open the generated
product.jsonfile and see if any format issues stands out?
-
It seems
pricefield is a string rather than float. The datatype is important, Lets correct it. -
To convert the price tag to a float in the JSON file, head back to the convert.js file and modify the code as below in line 21-27:
if (header === "tags") {
// Decode the JSON string
obj[header] = JSON.parse(values[index].replace(/'/g, '"'));
} else if (header === "price") {
// Convert price to integer
obj[header] = parseFloat(values[index], 10);
} else {
obj[header] = values[index];
} -
Execute the code again and compare the two JSON files once more.
note(Optional) Can you suggest a modification to the code that would preserve the quotation marks in the description field?
Bulk load product data
There are multiple options available for performing bulk operations in Cosmos DB. In this section, we will focus on using the bulkWrite method. The bulkWrite method allows you to execute multiple write operations in a single batch, including insert, update, and delete operations.
-
Open the
import.jsfile, and add the following code after the code blockconst db = client.db(dbname);. The code below is to be within the try-catch block.This will read the
product.jsonfile and load the data into theproductRawDatavariable. product.json file is used as it contains the fixes we made for price field. The database collection forproductis also initialized. Note that MongoDB will create the collections if they do not already exist.// Load product data
console.log("Loading product data");
// Initialize the product collection pointer (will automatically be created if it doesn't exist)
const productCollection = db.collection("products");
// Define the path to the local JSON file
const jsonFilePath = path.join("data", "product.json");
// Read the JSON file
const productRawData = fs.readFileSync(
path.join("data", "product.json"),
"utf8"
);
const productData = JSON.parse(productRawData).map((prod) =>
cleanData(prod)
); -
You may run the upload script multiple times, which will result in duplicate data. To avoid having duplicate data, the code below deletes any existing products before loading the new data.
// Delete any existing products
console.log("Deleting existing products");
await productCollection.deleteMany({});
var result = await productCollection.bulkWrite(
productData.map((product) => ({
insertOne: {
document: product,
},
}))
);
console.log(`${result.insertedCount} products inserted`); -
Save the
import.jsfile. -
Run the application by executing the following command in the terminal window:
node import.jstipWe reduced the total products in the data set from 295 to only 49 in the end. Do you know why?
Bulk load of customer and sales data
The Customer and Sales data is in the custSalesData.json file. We will be splitting the data into two collections, customers and sales, and loading them into Cosmos DB.
-
Open the
import.jsfile, and add the following code next to the previous code block. This will read thecustSalesData.jsonfile and load the data into thecustSaledDatavariable.The database collections for
customersandsalesare also initialized.// Load customer and sales data
console.log("Retrieving combined Customer/Sales data");
const customerCollection = db.collection("customers");
const salesCollection = db.collection("sales");
const custSalesRawData = fs.readFileSync(
path.join("data", "custSalesData.json"),
"utf8"
);
const custSalesData = JSON.parse(custSalesRawData).map((custSales) =>
cleanData(custSales)
); -
The following code firstly splits the
custSalesDataintocustomerandsalesdata, then loads the customer data into the collection using theinsertManymethod. Finally load the sales data into the collection using theinsertManymethod.console.log("Split customer and sales data");
const customerData = custSalesData.filter(
(cust) => cust["type"] === "customer"
);
const salesData = custSalesData.filter(
(sales) => sales["type"] === "salesOrder"
);
console.log("Loading customer data");
await customerCollection.deleteMany({});
result = await customerCollection.insertMany(customerData);
console.log(`${result.insertedCount} customers inserted`);
console.log("Loading sales data");
await salesCollection.deleteMany({});
result = await salesCollection.insertMany(salesData);
console.log(`${result.insertedCount} sales inserted`); -
Save the
import.jsfile. -
Run the application by executing the following command in the terminal window:
node import.js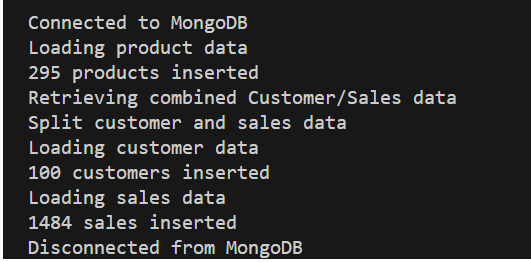
Browse the data in the Cosmos DB
-
If you are using VS Code locally, please install MongoDb extension, search
MongoDB for VS codeinExtensionstab. If you are using GitHub Codespaces, extension is already installed.
-
Add a connection to the data.
-
Browse the json records in the product and customer table.

In this section, we used bulk load operations to load product, customer, and sales data into Cosmos DB. We also had to cleanup the data before loading it into the database. In the next section, we will convert the data into embeddings and perform vector search on the data.