Workflow Orchestration using LangChain
In the previous lab, the mongodb package was used to perform a vector search through a db command to find product documents that were most similar to the user's input. In this lab, you will use the LangChain package to perform the same search. LangChain has a vector store class named AzureCosmosDBVectorStore, a community contribution, that supports vector search in Azure Cosmos DB.
The AzureCosmosDBVectorStore class represents a single vector index in the database, therefore for the instructions for this lab will focus on the products collection, however the same steps can be used with the customers and sales collections as well.
Throughout this lab, notice how much more concise the code is compared to the previous lab with the addition of LangChain.
Setup the lab environment
-
Navigate to the lab folder
~/labs/02-LAB-02/4-Using-Langchain/startwithin the repository.cd labs/02-LAB-02/4-Using-Langchain/startinfoThe
~/labs/02-LAB-02/4-Using-Langchain/completedfolder contains the completed solution for this lab. Please usestartfolder to carry out the exercise. You can compare your code with the files incompletedfolder if your code does not run correctly. -
Check
.envfile has correct configurations. Placeholder string should be all replaced in earlierLab Setupstep.infoThe Azure OpenAI service name is not the full endpoint. Only the service name is required. For example, if the endpoint is
https://myservicename.openai.azure.com/, then the service name ismyservicename. -
In Visual Studio Code, open a terminal window and navigate to the lab folder
start. -
Install the langchain packages by running the following command in the terminal window.
npm install langchain@0.1.21 --save
npm install @langchain/community@0.0.32 --save -
This will install the package and save it as a dependency in your project's
package.jsonfile. -
Install the required packages by running the following command in the terminal window:
npm install
Vector search with LangChain
The first step is to initialize the connection to the vector store. The AzureCosmosDBVectorStore class is used to represent the vector store. This section will walk through the initialization of this connection as well as a test call that issues a vector search and outputs the results.
When establishing the connection to the vector store, recall that in the previous lab, each collection was populated and a contentVector field added that contains the vectorized embeddings of the document itself. Finally, a vector index was also created on the contentVector field to enable vector search. The vector index in each collection is named VectorSearchIndex.
The return value of a vector search in LangChain is a list of Document objects. The LangChain Document class contains two properties: pageContent, that represents the textual content that is typically used to augment the prompt, and metadata that contains all other attributes of the document. In the cell below, we'll use the _id field as the pageContent, and the rest of the fields are returned as metadata.
-
Open the
vector-search.jsfile in the Visual Studio Code editor. -
Directly beneath the line
const { MongoClient } = require('mongodb');, add the following code to import the necessary LangChain packages. This code imports the AzureCosmosDBVectorStore that represents the vector index in a collection, theAzureCosmosDBSimilarityTypethat will allow us to perform a vector search using cosine similarity, and theOpenAIEmbeddingsclass that will be used to generate the embeddings for the user's input for the vector search.const {
AzureCosmosDBVectorStore,
AzureCosmosDBSimilarityType,
} = require("@langchain/community/vectorstores/azure_cosmosdb");
const { OpenAIEmbeddings } = require("@langchain/openai"); -
Directly beneath the line of code that sets up the MongoDB connection
const dbClient = new MongoClient(process.env.MONGODB_CONNECTION_STRING); var dbname = process.env.MONGODB_Name;, add the following code to initialize the connection to the vector store that points to theproductscollection and associated index. TheOpenAIEmbeddingsuses the default values obtained from the environment variables to initialize.// set up the Azure Cosmos DB vector store using the initialized MongoDB client
const azureCosmosDBConfig = {
client: dbClient,
databaseName: dbname,
collectionName: "products",
indexName: "VectorSearchIndex",
embeddingKey: "contentVector",
textKey: "_id",
};
const vectorStore = new AzureCosmosDBVectorStore(
new OpenAIEmbeddings(),
azureCosmosDBConfig
); -
In the
mainfunction, directly beneath the line of codeconsole.log("Connected to MongoDB");, append the following code that will perform a vector search using thevectorStoreobject and output the results.// perform a vector search using the vector store
const results = await vectorStore.similaritySearch(
"What yellow products do you have?",
AzureCosmosDBSimilarityType.CosineSimilarity,
3
);
console.log(results); -
Save the
vector-search.jsfile. -
Run the application by executing the following command in the terminal window:
node vector-search.jsThe output will be a list of
Documentobjects that contain the metadata of the documents that are most similar to the user's input.infoThe
Documentobjects contain thepage_contentandmetadataproperties. Thepage_contentis the_idfield of the document, and themetadatacontains all other fields of the document.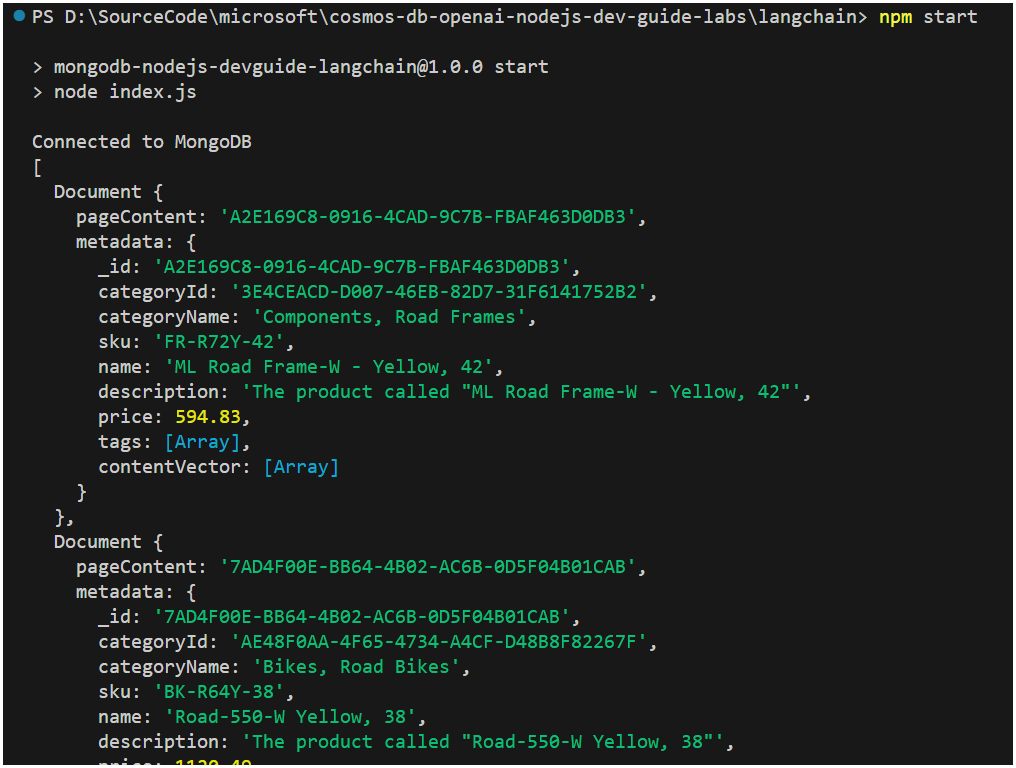 info
infoPlease compare
vectorStore.similaritySearchwith previous section'sragWithVectorsearch, can you tell the differences between them?
RAG with LangChain
In this section, we'll implement the RAG pattern using LangChain. In LangChain, a retriever is used to augment the prompt with contextual data. In this case, the already established vector store will be used as the retriever. By default, the prompt is augmented with the pageContent field of the retrieved document that customarily contains the text content of the embedded vector. In our case, the document itself serves as the textual content, so we'll have to do some pre-processing to format the text of the product list that is expected in our system prompt (JSON string) - see the formatDocuments function below for this implementation.
We'll also define a reusable RAG chain to control the flow and behavior of the call into the LLM. This chain is defined using the LCEL syntax (LangChain Expression Language).
-
Open the
langchain-rag.jsfile in the Visual Studio Code editor. -
Directly preceding the final line of code in this file (where the main function is called), add the
formatDocumentsfunction that will be used to format theDocumentobjects into a JSON string that will be used in the prompt for the LLM. The code is documented inline.function formatDocuments(docs) {
// Prepares the product list for the system prompt.
let strDocs = "";
for (let index = 0; index < docs.length; index++) {
let doc = docs[index];
let docFormatted = { _id: doc.pageContent };
Object.assign(docFormatted, doc.metadata);
// Build the product document without the contentVector and tags
if ("contentVector" in docFormatted) {
delete docFormatted["contentVector"];
}
if ("tags" in docFormatted) {
delete docFormatted["tags"];
}
// Add the formatted product document to the list
strDocs += JSON.stringify(docFormatted, null, "\t");
// Add a comma and newline after each item except the last
if (index < docs.length - 1) {
strDocs += ",\n";
}
}
// Add two newlines after the last item
strDocs += "\n\n";
return strDocs;
} -
Below
require("@langchain/community/vectorstores/azure_cosmosdb")import statement, add below class that will be used to interact with the LLM.const { OpenAIEmbeddings, ChatOpenAI } = require("@langchain/openai"); -
Directly beneath the line of code that was just modified in the previous step, add the following code to import and initialize an Azure OpenAI chat model.
// To support the LangChain LCEL RAG chain
const { PromptTemplate } = require("@langchain/core/prompts");
const {
RunnableSequence,
RunnablePassthrough,
} = require("@langchain/core/runnables");
const { StringOutputParser } = require("@langchain/core/output_parsers");
// set up the OpenAI chat model
const chatModel = new ChatOpenAI(); -
Before the last line of code in the file (that calls the main function), add the following function that creates a reusable LangChain RAG chain. The code is documented inline.
async function ragLCELChain(question) {
// A system prompt describes the responsibilities, instructions, and persona of the AI.
// Note the addition of the templated variable/placeholder for the list of products and the incoming question.
const systemPrompt = `
You are a helpful, fun and friendly sales assistant for Contoso Bike Store, a bicycle and bicycle accessories store.
Your name is Cosmo.
You are designed to answer questions about the products that Contoso Bike Store sells.
Only answer questions related to the information provided in the list of products below that are represented
in JSON format.
If you are asked a question that is not in the list, respond with "I don't know."
Only answer questions related to Contoso Bike Store products, customers, and sales orders.
If a question is not related to Contoso Bike Store products, customers, or sales orders,
respond with "I only answer questions about Contoso Bike Store"
List of products:
{products}
Question:
{question}
`;
// Use a retriever on the Cosmos DB vector store
const retriever = vectorStore.asRetriever();
// Initialize the prompt
const prompt = PromptTemplate.fromTemplate(systemPrompt);
// The RAG chain will populate the variable placeholders of the system prompt
// with the formatted list of products based on the documents retrieved from the vector store.
// The RAG chain will then invoke the LLM with the populated prompt and the question.
// The response from the LLM is then parsed as a string and returned.
const ragChain = RunnableSequence.from([
{
products: retriever.pipe(formatDocuments),
question: new RunnablePassthrough(),
},
prompt,
chatModel,
new StringOutputParser(),
]);
return await ragChain.invoke(question);
} -
In the
mainfunction, directly beneath the line of codeconsole.log('Connected to MongoDB');, add the following code that will call theragLCELChainfunction to perform a vector search using thevectorStoreobject and output the results.console.log(await ragLCELChain("What yellow products do you have?")); -
Save the
langchain-rag.jsfile. -
Run the application by executing the following command in the terminal window:
node langchain-rag.js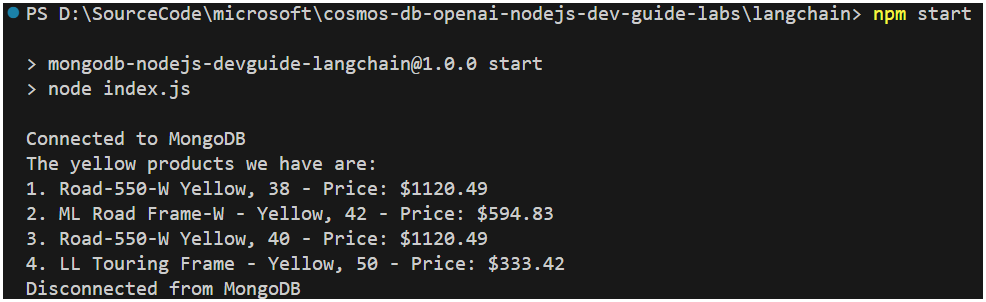
-
Lets now try a different question.
console.log(
await ragLCELChain(
"What is the name of the product that has the SKU TI-R982?"
)
);
Why do we get a response like this? how can we improve it?
LangChain agent
In this section, we'll implement a LangChain agent that will be used to interact with the LLM. The agent will be used to control the flow and behavior of the call into the LLM. An agent differs from the previous RAG chain in that the RAG chain is a definition of a sequence of specific actions. Agents on the other hand are equipped with various tools and will determine which actions to take based on the context of the conversation.
In this scenario, an agent will be equipped with two tools, one that uses a retriever chain from the vector store, and another that will perform a MongoDB lookup based on a SKU value. The reason the SKU lookup tool is introduced is because the vector store is built for semantic search. Some fields, such as the _id or sku fields do not have semantic meaning and therefore a direct lookup is more appropriate.
-
Open the
langchain-agent.jsfile in the Visual Studio Code editor. -
Immediately after the
const { StringOutputParser } = require("@langchain/core/output_parsers");line of code, add the following dependencies to support the creation of the LangChain agent:// For LangChain agent
const { DynamicTool } = require("@langchain/core/tools");
const { AgentExecutor } = require("langchain/agents");
const {
MessagesPlaceholder,
ChatPromptTemplate,
} = require("@langchain/core/prompts");
const {
convertToOpenAIFunction,
} = require("@langchain/core/utils/function_calling");
const {
OpenAIFunctionsAgentOutputParser,
} = require("langchain/agents/openai/output_parser");
const {
formatToOpenAIFunctionMessages,
} = require("langchain/agents/format_scratchpad"); -
Immediately before the last line of code in the file (that calls the main function), add the following function that builds a LangChain agent executor and a helper function that will invoke the agent. The code is documented inline.
async function buildAgentExecutor() {
// A system prompt describes the responsibilities, instructions, and persona of the AI.
// Note the variable placeholders for the list of products and the incoming question are not included.
// An agent system prompt contains only the persona and instructions for the AI.
const systemMessage = `
You are a helpful, fun and friendly sales assistant for Contoso Bike Store, a bicycle and bicycle accessories store.
Your name is Cosmo.
You are designed to answer questions about the products that Contoso Bike Store sells, the customers that buy them, and the sales orders that are placed by customers.
If you don't know the answer to a question, respond with "I don't know."
Only answer questions related to Contoso Bike Store products, customers, and sales orders.
If a question is not related to Contoso Bike Store products, customers, or sales orders,
respond with "I only answer questions about Contoso Bike Store"
`;
// Create vector store retriever chain to retrieve documents and formats them as a string for the prompt.
const retrieverChain = vectorStore.asRetriever().pipe(formatDocuments);
// Define tools for the agent can use, the description is important this is what the AI will
// use to decide which tool to use.
// A tool that retrieves product information from Contoso Bike Store based on the user's question.
const productsRetrieverTool = new DynamicTool({
name: "products_retriever_tool",
description: `Searches Contoso Bike Store product information for similar products based on the question.
Returns the product information in JSON format.`,
func: async (input) => await retrieverChain.invoke(input),
});
// A tool that will lookup a product by its SKU. Note that this is not a vector store lookup.
const productLookupTool = new DynamicTool({
name: "product_sku_lookup_tool",
description: `Searches Contoso Bike Store product information for a single product by its SKU.
Returns the product information in JSON format.
If the product is not found, returns null.`,
func: async (input) => {
const db = dbClient.db(dbname);
const products = db.collection("products");
const doc = await products.findOne({ sku: input });
if (doc) {
//remove the contentVector property to save on tokens
delete doc.contentVector;
}
return doc ? JSON.stringify(doc, null, "\t") : null;
},
});
const productFeedbackTool = new DynamicTool({
name: "product_feedback_lookup_tool",
description: `Searches Contoso Bike Store feedback based on the question.
Returns the product name, sku and feedback in text format.
If the product is not found, returns null.`,
func: async (input) => {
const url = `${graphRagAPI}/query/global`;
const requestBody = {
index_name: "bike",
query: `whats the top 2 products based on: ${input}?`,
community_level: 1
};
const response = await axios.post(url, requestBody, {});
return response.data.result;
},
});
// Generate OpenAI function metadata to provide to the LLM
// The LLM will use this metadata to decide which tool to use based on the description.
const tools = [productsRetrieverTool, productLookupTool, productFeedbackTool];
const modelWithFunctions = chatModel.bind({
functions: tools.map((tool) => convertToOpenAIFunction(tool)),
});
// OpenAI function calling is fine-tuned for tool using therefore you don't need to provide instruction.
// All that is required is that there be two variables: `input` and `agent_scratchpad`.
// Input represents the user prompt and agent_scratchpad acts as a log of tool invocations and outputs.
const prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.fromMessages([
["system", systemMessage],
["human", "{input}"],
new MessagesPlaceholder((variable_name = "agent_scratchpad")),
]);
// Define the agent and executor
// An agent is a type of chain that reasons over the input prompt and has the ability
// to decide which function(s) (tools) to use and parses the output of the functions.
const runnableAgent = RunnableSequence.from([
{
input: (i) => i.input,
agent_scratchpad: (i) => formatToOpenAIFunctionMessages(i.steps),
},
prompt,
modelWithFunctions,
new OpenAIFunctionsAgentOutputParser(),
]);
// An agent executor can be thought of as a runtime, it orchestrates the actions of the agent
// until completed. This can be the result of a single or multiple actions (one can feed into the next).
// Note: If you wish to see verbose output of the tool usage of the agent,
// set returnIntermediateSteps to true
const executor = AgentExecutor.fromAgentAndTools({
agent: runnableAgent,
tools,
//returnIntermediateSteps: true
});
return executor;
}
// Helper function that executes the agent with user input and returns the string output
async function executeAgent(agentExecutor, input) {
// Invoke the agent with the user input
const result = await agentExecutor.invoke({ input });
// Output the intermediate steps of the agent if returnIntermediateSteps is set to true
if (agentExecutor.returnIntermediateSteps) {
console.log(JSON.stringify(result.intermediateSteps, null, 2));
}
// Return the final response from the agent
return result.output;
} -
In the
mainfunction, directly beneath the line of codeconsole.log('Connected to MongoDB');, add the following code that will call thebuildAgentExecutorfunction to create the LangChain agent executor and theexecuteAgentfunction to engage with the agent and outupt the results.const agentExecutor = await buildAgentExecutor();
console.log(
await executeAgent(agentExecutor, "What yellow products do you have?")
); -
Save the
langchain-agent.jsfile. -
Run the application by executing the following command in the terminal window:
node langchain-agent.js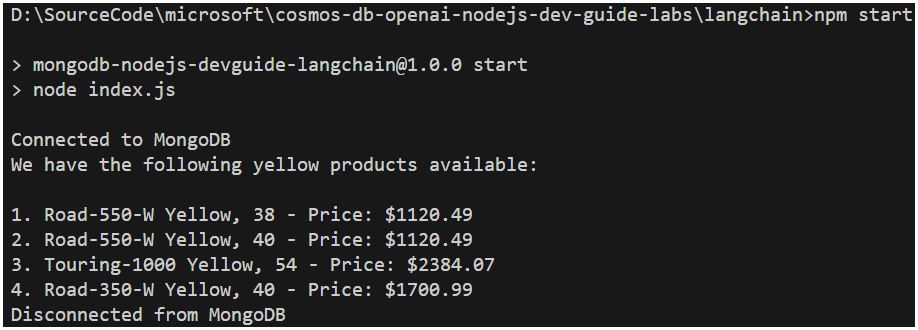
-
Change the question in the
executeAgentfunction toWhat is the name of the product that has the SKU TI-R982?. -
Find the commented line of code
//returnIntermediateSteps: truein theexecuteAgentfunction and uncomment it to enable verbose output of the tool usage of the agent. This will output the intermediate steps of the agent that includes the function calls and their outputs. -
Save the
langchain-agent.jsfile. -
Run the application by executing the following command in the terminal window:
node langchain-agent.js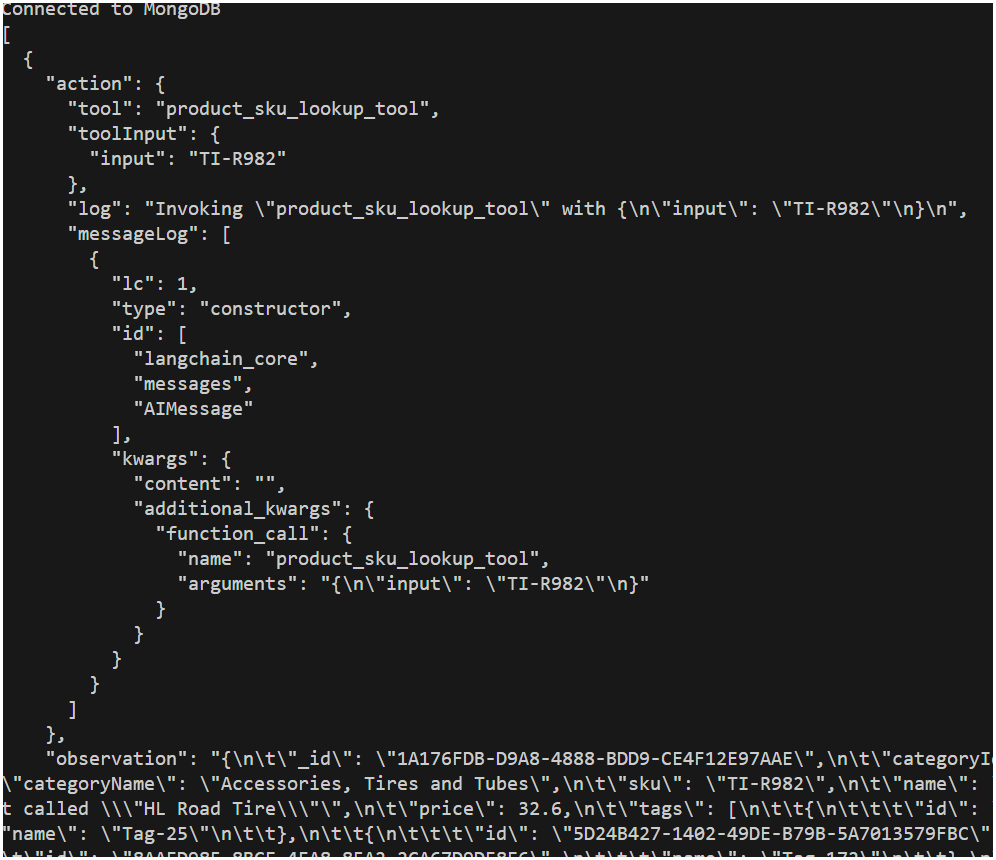
Notice the verbose output includes the selection, input, and observation(output) of the tool used by the agent.
-
If desired, comment out the line of code
//returnIntermediateSteps: truein theexecuteAgentfunction to disable verbose output of the tool usage of the agent.
Please think about the difference between langchain-rag.js and langchain-agent.js. Which one do you think is better?
- Experiment with additional questions of your own. For example, change the question in the
executeAgentfunction toWhat's the top 2 Tire based on feedback?. It will useproductFeedbackToolto invoike API call to Graph RAG endpoint.
Summary
In this lab, you used the LangChain package to perform a vector search in Azure Cosmos DB. You initialized the connection to the vector store, performed a vector search, implemented the RAG pattern using LangChain, and created a LangChain agent. You also experimented with the LangChain agent and observed the verbose output of the tool usage of the agent.